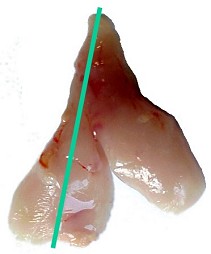
Thymus, young rat.
| Species: | Rats and Mice |
| Organ: | Thymus |
| Localizations: | Along the length of one lobe Option: whole organ |
| Number of sections: | 1 |
| Direction: | Longitudinal |
| Remarks: | Largest area Thymic region in old animals |
 Thymus, young rat. |
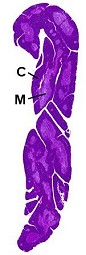 Thymus (C: cortex, M: medulla). |
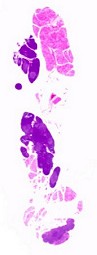 Atrophic thymus. |
The whole thymus is fixed and trimmed along the length of one lobe. This gives a standardized longitudinal section showing all anatomical structures of this organ.
In immuno-toxicological assays, it is advisable to embed the whole organ, ventral aspect down, and to cut both lobes. In case of thymic atrophy or involution, the whole organ / thymic region should be embedded.
See also:
Introduction
|
Trm V 5.00 |
Reference: Morawietz G, Ruehl-Fehlert C, Kittel B, et al. (2004) Revised guides for organ sampling and trimming in rats and mice – Part 3. A joint publication of the RITA and NACAD groups. Exp Toxic Pathol 55: 433–449 |